Code vs Serialized AST Inputs for LLM-Based Code Summarization: An Empirical Study (to appear)
Abstract
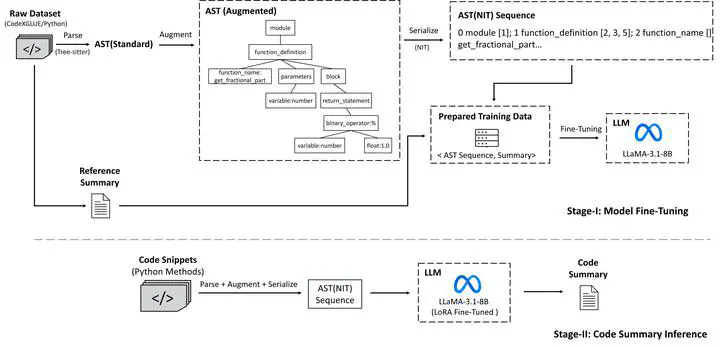
Summarizing source code into natural language descriptions (code summarization) helps developers better understand program functionality and reduce the burden of software maintenance. Abstract Syntax Trees (ASTs), as opposed to source code, have been shown to improve summarization quality in traditional encoder–decoder-based code summarization models. However, most large language model (LLM)-based code summarization methods rely on raw code or only incorporate partial AST signals, meaning that the potential of complete AST representation has not been fully explored for LLMs.
This paper presents AST(NIT), an AST augmentation and serialization method that preserves lexical details and encodes structural information into LLM-compatible sequences. Experiments with the LLaMA-3.1-8B model on the CodeXGLUE Python dataset show that the proposed serialized ASTs reduce the length of LLM inputs, require shorter training times, and achieve summarization quality comparable to existing approaches."